In this post I’ll show you how to expose your “Daprized” applications using and NGINX ingress controller.
Prerequistes#
- A working kubernetes cluster with Dapr installed. If you need instructions please find them here
Deploy an application to your Kubernetes cluster#
I’ll be using a simple Azure Function I created back in 2017 in the following post: Run a Precompiled .NET Core Azure Function in a Container which exposes a simple validation function.
Create a function.yaml file with the following contents:
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: dni-function
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: dni-function
annotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/id: "dni"
dapr.io/port: "80"
spec:
containers:
- name: dni-function
image: cmendibl3/dni:1.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80Note the dapr.io annotations used to instruct Dapr to inject the sidecar in your pod.
Now deploy the function into kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f ./function.yamlDeploy NGINX Ingress Controller with Dapr#
We are going to “Daprize” the NGINX Ingress Controller so traffic flows as shown in the following picture [1]:
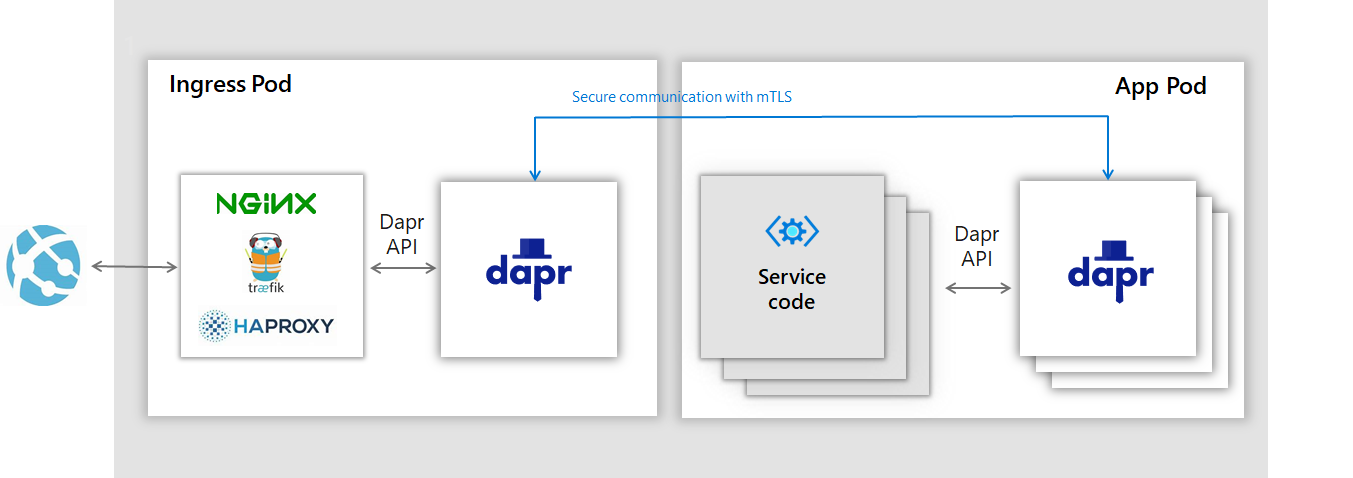
In order to add the dapr.io annotations to the NGINX pod, create a dapr-annotations.yaml file with the following contents:
controller:
podAnnotations:
dapr.io/enabled: "true"
dapr.io/id: "nginx-ingress"
dapr.io/port: "80"and deploy the NGINX ingress controller:
helm repo add stable https://kubernetes-charts.storage.googleapis.com/
helm install nginx stable/nginx-ingress -f .\dapr-annotations.yaml -n defaultSince we´ll also be adding TLS termination to the mix, run the following commands to generate the certificate and deploy the corresponding secret into kubernetes:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout tls.key -out tls.crt -subj "/CN=hydra/O=hydra"
kubectl create secret tls tls-secret --key tls.key --cert tls.certNow create the ingress rule (ingress.yaml* file) with the following contents:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-rules
namespace: default
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- hydra
secretName: tls-secret
rules:
- host: hydra
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: nginx-ingress-dapr
servicePort: 80Note that the rule is calling the nginx-ingress-dapr service which was created by Dapr when we deployed the Daprized version of the ingress controller. This means that all trafic with the hydra host will be sent to the Dapr sidecar of your NGINX controller pod.
Deploy the ingress rule:
kubectl apply -f ./ingress.yamlTest the “Daprized” application#
To test the application we’ll need the public IP of the ingress service, so run the following command and copy the resulting IP address:
kubectl get service --selector=app=nginx-ingress,component=controller -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'Now make a simple curl request, using the Dapr invocation api specification, to the application:
curl -k -H "Host: hydra" "https://<ingress ip>/v1.0/invoke/dni/method/api/validate?dni=54495436H"If everything runs as expected you should get the following result:
trueHope it helps!
Learn more about Dapr here and Dapr service invocation here
Learn More#
- How Distributed Application Runtime (Dapr) has grown since its announcement
- Announcing Azure Functions extension for Dapr
References#
[1] Image from the Dapr Predentation deck
