Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server allows configuring high availability with automatic failover. With Zone-redundant HA your service has redundancy of infrastructure across multiple availability zones.
Zone-redundant HA is preferred when you want to achieve the highest level of availability against any infrastructure failure in the availability zone and when latency across the availability zone is acceptable.
Today I’ll show hot to test the failover of a zone-redundant MySQL Flexible Server instance.
Deploy Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server with availability zones#
Create a main.tf file with the following content:#
terraform {
required_version = "> 0.14"
required_providers {
azurerm = {
version = ">= 2.87.0"
}
random = {
version = "= 3.1.0"
}
}
}
provider "azurerm" {
features {}
}
# Location of the services
variable "location" {
default = "west europe"
}
# Resource Group Name
variable "resource_group" {
default = "mysql-failover"
}
# Name of the mysql cluster
variable "mysql_name" {
default = "mysql-failover"
}
resource "random_id" "random" {
byte_length = 8
}
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = var.resource_group
location = var.location
}
data "http" "current_public_ip" {
url = "http://ipinfo.io/json"
request_headers = {
Accept = "application/json"
}
}
resource "azurerm_mysql_flexible_server" "flexible_server" {
name = "${var.mysql_name}-${lower(random_id.random.hex)}"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
administrator_login = "psqladmin"
administrator_password = "H@Sh1CoR3!"
backup_retention_days = 7
sku_name = "GP_Standard_D2ds_v4"
high_availability {
mode = "ZoneRedundant"
standby_availability_zone = "2"
}
zone = "1"
}
resource "azurerm_mysql_flexible_server_firewall_rule" "ip" {
name = "home"
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
server_name = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.name
start_ip_address = jsondecode(data.http.current_public_ip.body).ip
end_ip_address = jsondecode(data.http.current_public_ip.body).ip
}
resource "azurerm_log_analytics_workspace" "logs" {
name = "mysql-logs"
location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location
resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name
sku = "PerGB2018"
retention_in_days = 30
}
resource "azurerm_monitor_diagnostic_setting" "monitor" {
name = lower("extaudit-${var.mysql_name}-diag")
target_resource_id = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.id
log_analytics_workspace_id = azurerm_log_analytics_workspace.logs.id
metric {
category = "AllMetrics"
retention_policy {
enabled = false
}
}
log {
category = "MySqlAuditLogs"
enabled = false
retention_policy {
days = 0
enabled = false
}
}
log {
category = "MySqlSlowLogs"
enabled = false
retention_policy {
days = 0
enabled = false
}
}
lifecycle {
ignore_changes = [metric]
}
}
output "resource_group" {
value = var.resource_group
}
output "mysql_name" {
value = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.name
}
output "mysql_fqdn" {
value = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.fqdn
}
output "administrator_login" {
value = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.administrator_login
sensitive = true
}
output "administrator_password" {
value = azurerm_mysql_flexible_server.flexible_server.administrator_password
sensitive = true
}Note:
zone = "1"sets the primary availability zone.high_availability.mode = "ZoneRedundant"enables availability zone redundancy.high_availability.standby_availability_zone = "2"sets the stanby availability zone
For convinience, I added the password to the terraform configuration. Please don’t repeat this in your environment.
Deploy the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server with availability zones:#
Run the following command to deploy the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server with availability zones:
terraform init
terraform apply -auto-approveTest the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server failover#
Create a Database:#
resource_group=$(terraform output -raw resource_group)
mysql_name=$(terraform output -raw mysql_name)
az mysql flexible-server db create --resource-group $resource_group --server-name $mysql_name --database-name failover_databaseCheck Database Connectivity:#
mysql_name=$(terraform output -raw mysql_name)
mysql_user=$(terraform output -raw administrator_login)
mysql_password=$(terraform output -raw administrator_password)
az mysql flexible-server connect -n $mysql_name -u $mysql_user -p $mysql_password -d failover_databaseCheck the availability zone hosting the primary database:#
resource_group=$(terraform output -raw resource_group)
mysql_name=$(terraform output -raw mysql_name)
az mysql flexible-server show -n $mysql_name -g $resource_group --query "availabilityZone" -o tsvyou should get the following output:
1Test the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server failover (Azure Portal):#
To force the failover head to the Azure portal and use the Settings / High Availabilitysection of the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server and click on Forced Failover:
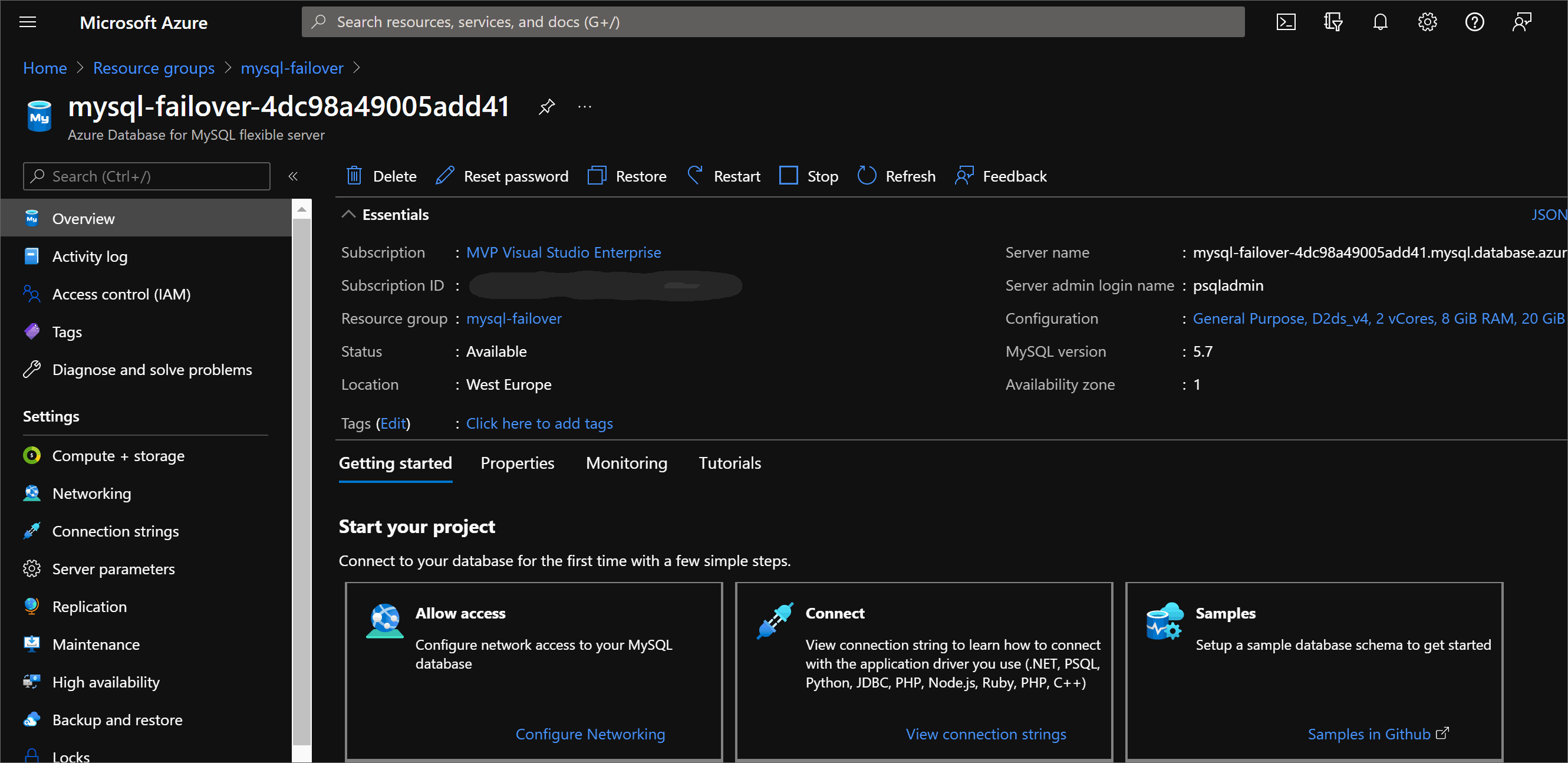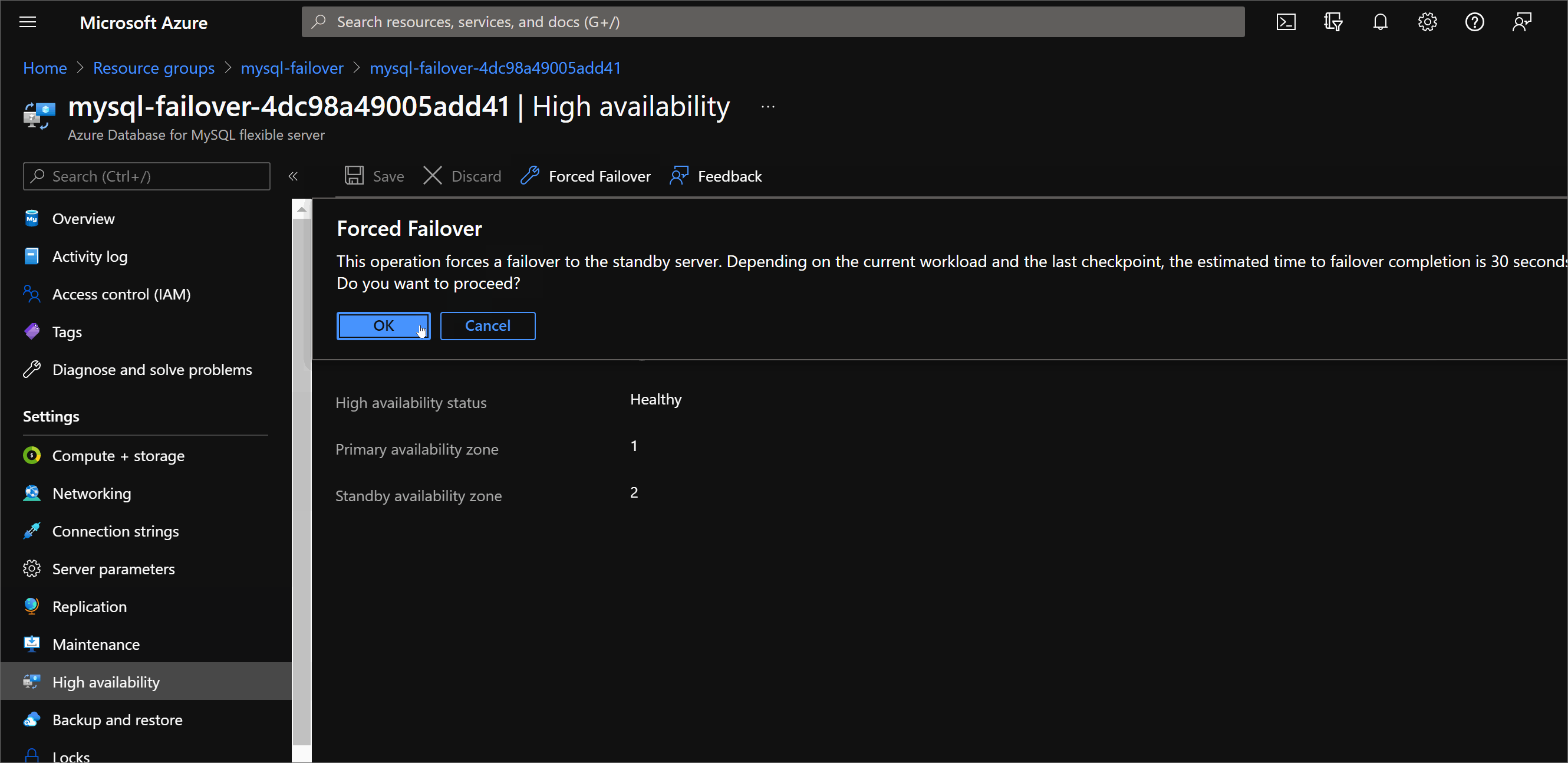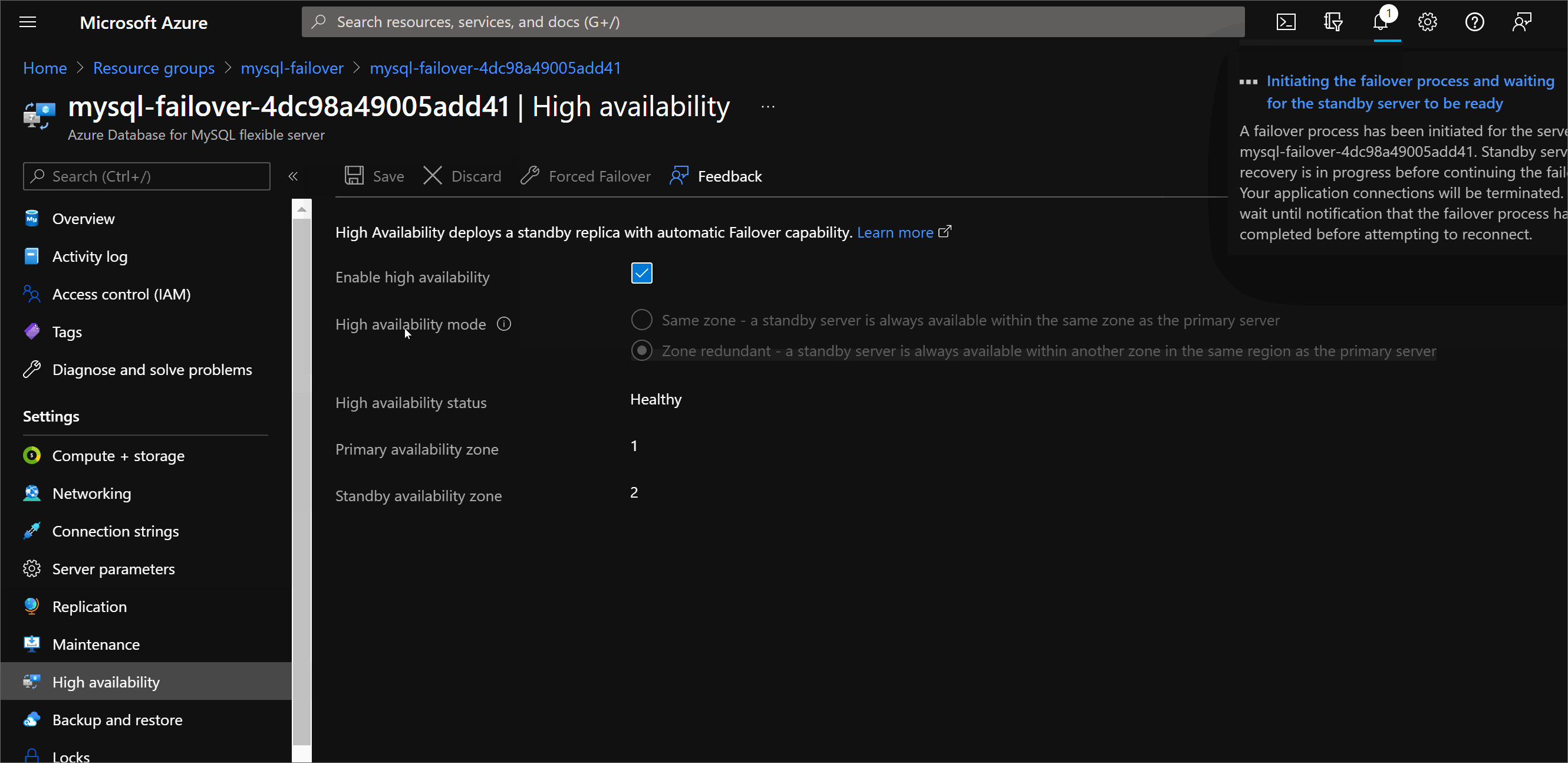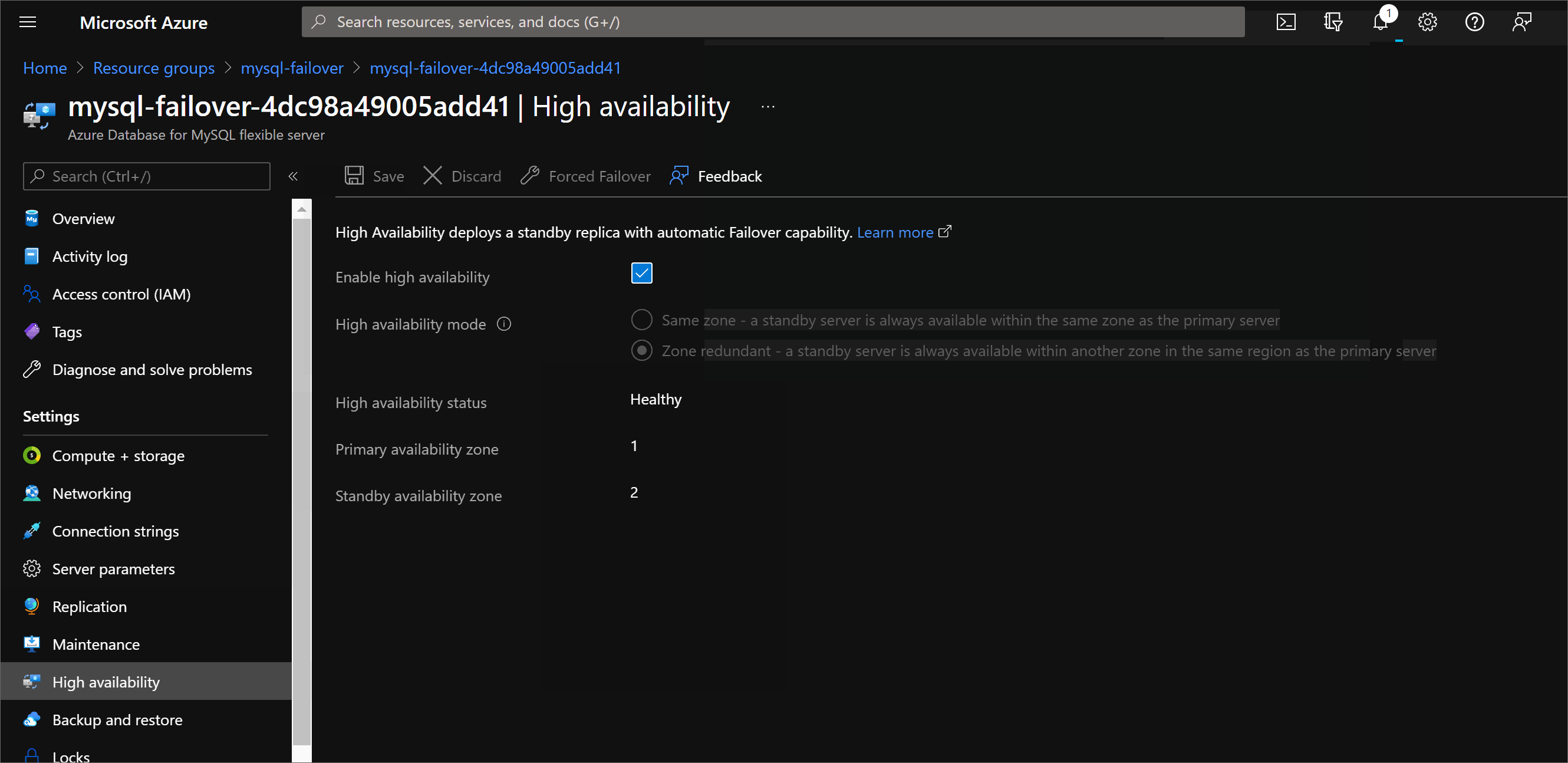
Once failover start and the database becomes unavailable, the standby replica is activated as the primary database, DNS is updated, and clients must reconnect to the database server and resume their operations.
This process should take between 60 and 120 seconds. But, depending on the activity in the primary database server at the time of the failover, the failover might take longer.
Once the failover is complete, check again which availability zone hosts the primary database:
resource_group=$(terraform output -raw resource_group)
mysql_name=$(terraform output -raw mysql_name)
az mysql flexible-server show -n $mysql_name -g $resource_group --query "availabilityZone" -o tsvthe output should be:
2Hope it helps!!!
References:
